Introduction
In recent years, the effects of climate change have become increasingly evident across the globe. As a result, nations, cities, and communities are now focusing on strategies for climate change adaptation and resilience. In this regard, surveying and mapping technologies play an essential role. By providing precise data on environmental variables, these tools enable decision-makers to implement effective solutions. Thus, understanding how surveying and mapping contribute to climate adaptation and resilience is crucial for mitigating the impacts of climate change.
1. Understanding Climate Change Adaptation and Resilience
First, let’s define climate change adaptation and resilience. Climate adaptation refers to the process of adjusting to the adverse effects of climate change, while resilience focuses on the ability to recover from such changes. Both are critical components of a comprehensive climate strategy. Furthermore, it’s important to recognize that without these measures, communities face heightened risks such as extreme weather events, sea-level rise, and ecosystem disruptions. Therefore, proactive approaches, such as the integration of mapping and surveying, are vital for reducing long-term risks and safeguarding the environment.
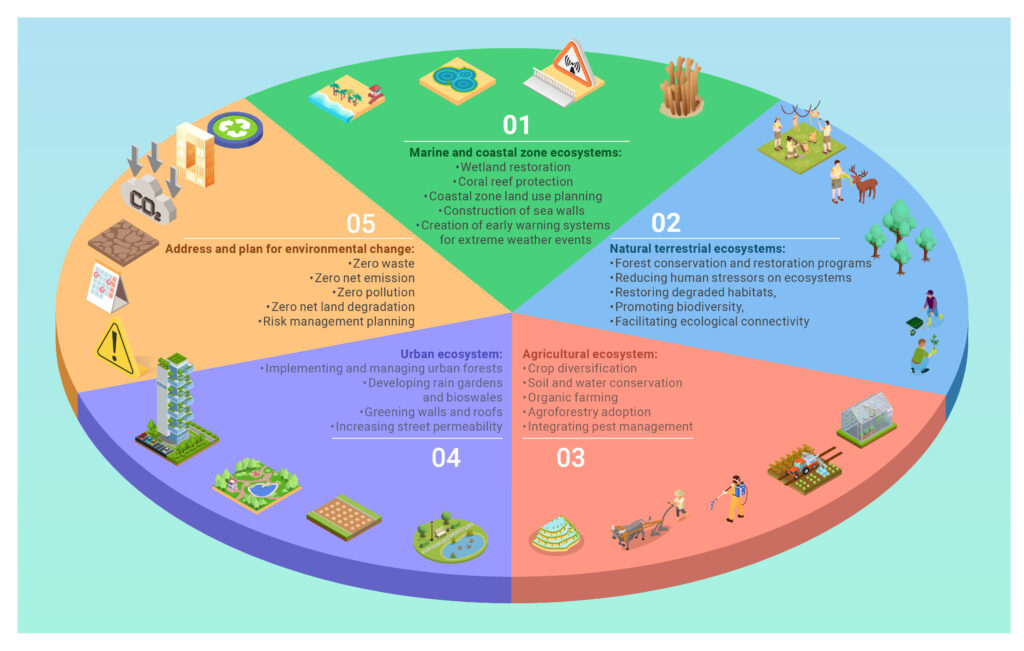
2. chttp://The Role of Land Surveying in Environmental Conservation
Surveying technologies, such as land surveys and remote sensing, provide critical data needed for climate adaptation. For instance, accurate mapping of elevation and land contours can help identify flood-prone areas, enabling better planning for infrastructure development. Additionally, surveys that track environmental changes over time allow experts to monitor trends, such as shifts in vegetation or soil moisture. This information is invaluable for urban planners and policymakers who need to make informed decisions. Moreover, land surveys can also assess the impact of human activity on ecosystems, facilitating efforts to restore and protect vulnerable areas.
3. Mapping Technologies for Climate Resilience
Mapping technologies, including Geographic Information Systems (GIS), satellite imagery, and LiDAR, are essential tools in building climate resilience. For example, GIS can overlay different types of data, such as population density, flood risk, and infrastructure, to identify high-risk zones and prioritize actions. Moreover, satellite imagery provides real-time insights into changes in the environment, such as deforestation, water level variations, and coastal erosion. Thus, mapping not only helps in planning, but it also provides early warning systems to mitigate disaster impacts. In addition, LiDAR technology, which uses laser sensors, can map terrain with incredible precision, offering more detailed insights into flood and landslide risks.

4. Case Studies: Surveying and Mapping in Action
There are several case studies where surveying and mapping have proven vital in climate change adaptation efforts. For instance, in the Netherlands, flood risk mapping has allowed for the construction of flood barriers and water management systems that protect vulnerable communities. Similarly, in California, satellite imagery has been used to monitor drought conditions and water resource management. These examples highlight how effective mapping and surveying are in both disaster prevention and in managing ongoing climate risks.
5. How Surveying and Mapping Contribute to Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
The role of surveying and mapping also aligns with several of the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG #13 (Climate Action) and SDG #11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities). By integrating these technologies, countries and communities can monitor their progress in mitigating climate risks and building resilience. For example, climate data gathered from surveys and maps can guide policies aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions, improving infrastructure, and enhancing resource management. Consequently, these tools support not only climate adaptation but also broader sustainability initiatives.
6. Future Directions: Innovations in Surveying and Mapping for Climate Change
The future of surveying and mapping in climate change adaptation looks promising. Emerging technologies such as AI, real-time data processing, and autonomous mapping systems will further enhance the accuracy and speed of data collection. For instance, AI can help predict climate trends and model disaster scenarios more effectively. Additionally, advancements in remote sensing and communication technologies will allow for better coordination in emergency response and resilience-building activities. Ultimately, these innovations will enable more adaptive and proactive strategies for mitigating the impacts of climate change.
Conclusion
In conclusion, surveying and mapping play an indispensable role in climate change adaptation and resilience. By providing valuable data on environmental changes and vulnerabilities, these tools enable communities and governments to take informed action. Moreover, as technological innovations continue to advance, the ability to anticipate, plan for, and respond to climate-related challenges will improve significantly. Thus, investing in these technologies is essential for building a more resilient and sustainable future in the face of climate change.
