Introduction: The Growing Role of Thermal Mapping in Conservation
In recent years, thermal mapping in environmental monitoring has become a crucial tool for conservationists and environmentalists alike. By using infrared sensors to map temperature variations across natural landscapes, this technology helps track and protect ecosystems more effectively. Thermal mapping allows scientists to monitor everything from wildlife movements to forest health, providing vital data for early intervention. In this blog, we’ll explore how thermal mapping plays a pivotal role in environmental monitoring and conservation, helping to preserve biodiversity and maintain ecological balance.
Thermal mapping involves the process of capturing temperature data across large landscapes using infrared sensors. These sensors detect temperature differences in both land and water, providing valuable information about the health of the environment. To gather this data, experts typically rely on drones, satellites, or planes equipped with thermal imaging technology. These systems create detailed maps that highlight temperature changes, allowing researchers to identify environmental stressors in real-time.
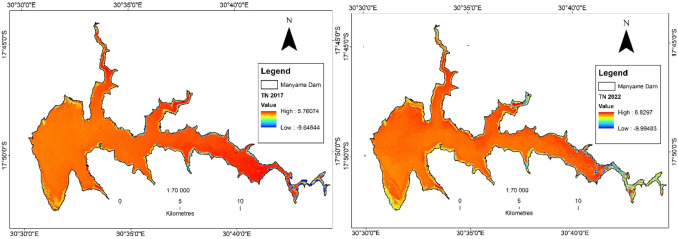
What is Thermal Mapping and How Does It Work?
Understanding the Technology Behind Thermal Mapping
The core of thermal mapping technology lies in infrared radiation, which objects emit based on their temperature. Warmer objects release more radiation. By capturing this data, experts can visualize temperature differences that may indicate areas of concern. For instance, thermal mapping can detect heat signatures of animals, track the health of forests, or monitor bodies of water. This technology empowers researchers to act quickly, addressing environmental issues before they escalate.
The Importance of Thermal Mapping in Environmental Monitoring
Thermal mapping plays a crucial role in environmental monitoring. It allows researchers to track various environmental factors in real-time, such as:
- Water temperature: Vital for monitoring aquatic ecosystems and aquatic species.
- Forest health: Helps detect temperature changes caused by diseases, pests, or droughts.
- Wildlife movements: Tracks the heat signatures of animals, aiding in their study and protection.
By continuously monitoring these factors, thermal mapping helps identify early signs of environmental threats. Early detection allows experts to implement timely interventions to protect ecosystems.
Applications of Thermal Mapping in Conservation Efforts
In conservation, thermal mapping provides numerous applications. For example, it plays an essential role in monitoring coral reefs. Rising sea temperatures can lead to coral bleaching, which threatens marine biodiversity. By using thermal mapping, scientists can pinpoint hot spots in the ocean, allowing them to take preventative measures.
Real-World Examples of Thermal Mapping in Conservation
In Africa, thermal mapping has been used to track and protect elephant populations. By detecting the heat signatures of elephants, conservationists can monitor their movements at night and ensure that they stay within protected areas. Similarly, thermal mapping has been used in rainforests to monitor orangutans. Researchers use the technology to track their movements and prevent illegal poaching and habitat destruction.
Benefits of Using Thermal Mapping for Biodiversity and Habitat Preservation
Thermal mapping offers several benefits for biodiversity and habitat preservation:
- Accurate Habitat Mapping: It helps scientists identify crucial habitats and ensures that conservation efforts focus on the right areas.
- Wildlife Stress Monitoring: By detecting temperature changes, researchers can monitor stress levels in species, identifying when and where intervention is necessary.
- Efficient Data Collection: Thermal mapping enables large-scale monitoring, which reduces the time and costs involved in traditional methods like ground surveys.
Future Trends: How Thermal Mapping Will Shape Environmental Conservation
As technology advances, thermal mapping continues to evolve. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning will make data analysis faster and more accurate. These technologies will help conservationists predict potential environmental changes, allowing for proactive measures.
Challenges in Implementing Thermal Mapping for Monitoring
Despite its benefits, thermal mapping does present some challenges. One of the main obstacles is the cost of the technology, as infrared sensors and drones can be expensive. Additionally, weather conditions such as heavy rain or cloud cover can interfere with the accuracy of thermal data, making it difficult to gather information in certain conditions.
Conclusion: Why Thermal Mapping is Crucial for Conservation Success
In conclusion, thermal mapping in environmental monitoring plays a vital role in preserving ecosystems and biodiversity. By offering detailed insights into environmental conditions, this technology enables conservationists to act swiftly and protect at-risk habitats. As the technology continues to evolve, thermal mapping will remain an essential tool in the fight to conserve the planet’s natural resourcesural resources.
